Introduction to Programming and Data Structures
encryption
one-time pad
bitwise XOR: bitwise exclusive or
∧ caret (\wedge)
Boolean algebra
pseudo-random
pseudo random bits:
linear feedback shift register LFSR
bit, cell, register, seed, initial state
[N, k] LFSR: N-bit register with taps at N and k
seed cannot be 0, at most 2N − 1 fills in N-bit register
k counts from 1…
Java programming
virtual terminal vs integrated development environment IDE
Java program shell:
public class program_name {
public static void main(String[] args) {//begin
body
}//end
}
piping and redirecting—|, <, >
| is two directional
< and > take one’s output as the other one’s input, following the arrow
for multiple piping, “parenthesis” are added as if
convert to type: Type.parseType(String_needs_converting)
cast: (type) what_needs_converting
does not convert type when divide
convert to the more precise type when operate between two types
int
Integer.MAX_VALUE + 1 = Integer.MIN_VALUE =-Integer.MIN_VALUE
remainder %
char—uses ASCII, can be operated as if int, cast to int if not assigned to a char
a~z, A~Z, 0~9 are together in ASCII, this can give a range
char array converts to String when called String.valueOf()
StringBuilder—better way to concatenate strings
concatenate strings: .append
double
special values: Infinity, NaN
math library
type operation(type variable, …)
type: double, int, long, float
operation: abs, max, sin, asin, exp, log, pow, round, random, sqrt
variable: a, PI, E
boolean operation
and &&
or ||
not !
xor (!a && b) || (a && !b)
(a && b) == (!(!a || !b))
naming
camel case: moreThanOneWord
constant: MORE_THAN_ONE_WORD
loop
if if (boolean) {execution1;}
else {execution2;}
while while (boolean)
{
execution1
}
for for (initialization_statement1, …; boolean; increament_statement1, …)
{
execution
}
switch switch (variable) {
case literal -> operation;
…
}
do while do {execution1} while (boolean);
at least does once
array
type[] name;//declare array name of type type
new double[length];//an array of length length, all 0.0s
name[index] = literal//refer to array name by index index
{literal1,…}//an array
.length
copy: copy the length and every single value
assign: refer to the same array
two dimentional array
double[][] a
a[0].length decide all a[i].length
sorting: Arrays.sort()
output: System.out.println(output)//print output \n
System.out.print(output)//print output
System.out.printf(“string1%w1.p1c1… string2”,output1,…)//print string1 output1… string2 with field width w, precision .p, and conversion code c
negative w counts from the right. for c, d: decimal, f: floating, e: scientific, s: string, b: boolean
must have % and c
this is the standard string format in Java
https://docs.oracle.com/javase/tutorial/java/data/numberformat.html
DecimalFormat df = new DecimalFormat(“##.##”);
StdDraw line(,,,), point(,),
setCanvasSize(w,h), setXscale(x0,x1), setPenRadius(),
shape, filledShape
text(x,y,String)
enableDoubleBuffering, show, clear, pause,
System.exit(0); makes the program stop
input:
command-line argument: args[No.] //input in modyfy run configuration - program argument
StdIn: isEmpty, readType, readAllTypes, hasNextChar, hasNextLine*//Type = Int, Double, Boolean, String, or Line*
scanner:import java.util.Scanner; //import scanner
Scanner sc= new Scanner(System.in); //define a scanner
Type variable = sc.nextType();//let variable be input
make an explanation
/*
*
/
function
static void can change content of array as they are mutable, cannot change value of primitive type as they are immutable
import static imports the method so that its prefix can be ommited don’t use
applications programming interface API
private static long[] makes the array global
call: ClassName.method(object)
final makes the variable immutatble
recursion
recurrence relation
Gray codes: show all n-digit binary numbers by only changing 1 digit at a time
start from i = 0, change the ith digit from 0 to 1 and do everything done to the first i − 1 digits backwards
recursive graph
fractal
Brownian bridge: random path to bridge to points
midpoint displacement method: take the midpoint and Gaussianly-randomly move it, and set it as one of the end point
volatility: initial variance of the Gaussian dist
Hurst exponent H: divide the variance of the Gaussian dist by 22H H is ½ for Brownian bridge
fractal dimension: 2 − H
plasma clouds
exponential waste: calculate the same thing again
dynamic programming
store calculated results in array
top-down solution
make global array and recursion
bottom-up solution
make local array and loop
longest common subsequance LCS problem
for x[i…m) and y[j…n),
percolation
Monte Carlo simulation: apply randomness to estimate unknown qualities by simulation
2-dimentional n by n sites
blocked site, open site; full site, empty site
site vacancy probability p
vertical percolation: go straight down
object
reference type vs primitive type
create object: ClassName reference = new ClassName(argument1,argument2,…)
Color
import java.awt.Color;
Color(r,g,b)
col.getBlue()
Luminance Y = 0.299r + 0.587g + 0.114b
reference type
aliasing—pass by value
orphaned object: don’t have a reference
instance method: data-type operation for reference type
reference.method(argument)
create data-type
public class ClassName {
*// instance variable inside the reference type (not final if need to change value)
*private final type instanceVariable1;
…
*// constructor, with the same name as the class
*public ClassName(type parameterVariable1, …) {
type localVariable = value;
instanceVariable1 = parameterVariable1;
…
}
/*
- explanation of the method
*/
*public double methodName(type argument1, …) {
…
return something;
}
use short name for instance variables for convenience
use full name for parameter variables as the client can see them
immutability: final makes the value of primitive type and the identity of the object of reference type immutable
defensive copy: copy each of the values of the parameter variables to avoid aliasing
interface type
public interface interfaceName {
public abstract type methodName(type parameterVariable);
}
abstract methods: includes nothing
implements
public class ClassName implements interfaceName{
public int methodName(type parameterVariable) {
}
}
the class must have methods coresponding to all abstract methods in the interface
interface enables a method name to call different methods according to the object
functional interface: single method
lambda expression
(parameterVariable1,…) -> stuffToReturn;
implementation inheritance
subclass
general equals method
public boolean equals(Object x)
{
if (x == null) return false;
if (this.getClass() != x.getClass()) return false;
Class that = (Class) x;
return (this.instanceVariable1 == that.instanceVariable1) && …;
}
general hashcode method
public int hashCode() {
return Objects.hash(instanceVariable1,…);
}
wrapper type: built-in reference type corresponding to primitive type
autoboxing and unboxing
performance
running time: time when finish minus time when start (in millisecond)
System.currentTimeMillis()
System.nanoTime()
algorithm
tilde notation ∼ f(n)
order of growth
empirical analysis
doubling hypothesis: double the input size, study the running time
mathematical analysis
memory usage: bool—1; char—2; int, float, padding—4; long, double, object reference—8; object overhead—16; array overhead—24 (b)
big-O notation O(g(n)): running time |f(n)| < c|g(n)| ∀ n > n0
binary search
exception filter—determine whether a name is in a sorted array
collection
operations—create, insert, remove, test emptiness
item
(pushdown) stack
last-in-first-out (LIFO)
operations—push, pop, test emptiness
queue
first-in-first-out (FIFO)
linked-list
node—content + next node
iterator
resizing array—double the size if no enough space, halve it if less than ¼ used
avoid loitering—set the variable to null
generic type
generic class—a class that can be fed with different data types
public class GenericClass<typeParameter>
type parameter—a name for the data type to be used in this class by the client
constructor
public GenericClass(typeParameter parameter**)
{
para = parameter;
…
}
using the constructor
GenericClass<String> variableName = new GenericClass<String>(“blah”)**;
symbol table
key-value pairs—cannot be null
get(key)/ put(key,val)
contains(key)
hashing
binary search tree BST
put
get
regular expression
minimum RE
concatenate
union—| or {…,…}
closure—x*
grouping—()
java REs
String.matches(regex)
Pattern pattern = Pattern.compile(RE)
Matcher matcher = pattern.matcher(input)
matcher.find()
matcher.matches()
shorthands
wildcard—.
beginning of line—^
end of line—$
range—[char1-char2]
negation—^x
closure operator extension
one or more—x+
zero or one—x?
length—{num}
between—{low, high}
deterministic finite-state automata DFA
finite number of states
transitions
tape reader
universal virtual DFA
input format—number of states \s alphabet \s one line of each state
nondeterministic finite-state automata DFA
pushdown automaton PDA
Turing machine
universality
computability
David Hilbert’s questions: mathematics is consistent, complete, decidable?
Kurt Gödel: axiomatic system cannot be both consistent and complete
Alan Turing: mathematics is not complete
halting problem—reductio ab absurdum
totality problem, equivalence problem
Henry Rice: determining whether a program has any given functional property is unsolvable
intractability—no algorithm exists to efficently solve
polynomial-time algorithm—bounded above by a**nb—efficient
exponential-time algorithm—bounded below by 2a**nb
satisfiability problems
search problems—the problems with solutions that polynomial-times algorithms can check
NP—the set of all search problems
NP-complete—every search problems polynomial-time reduces to it
P—the set of all search problems that can be solved in poly-time
representation
binary—0b
convert to binary and print—System.out.print(String.format(“%16s”, Integer.toBinaryString(number)).replace(’ ’, ‘0’));
hexadecimal—0x
read hexadecimal—Integer.parseInt(input, 16)
twos-complement—−x = ∼ x + 1
∼ x—complement, flip all bits
arithmetic shift right—add 1 to begin if negative
logical shift right—always add 0
masking—get the bits wanted by bitwise or with a mask that only has 1s in the corresponding bits
TOY machine
16 bit
memory
memory location M[00] ∼ M[F**F]
memory dump M[F**F]—standard IO
arithmetic and logic unit ALU
computation engine
register
16 words R[0] ∼ R[F]
connect ALU & memory
R[0] is always 0
program counter PC
8 bit
memory address of next instruction
instruction register IR
current instruction
fetch-inctemenat-execute cycle
fetch from memory to IR
increment PC
execute as IR says and change memory or PC or calculate
instruction format (16 bit)
type RR—opcode + 3 registers (destination + 2 sources)
arithmetic instruction—1, 2 for addition, subtraction
logical instruction—3~6
type A—opcode + register (destination) + memory address (8 bits)
memory address instruction—7, A, B
memory instruction—8, 9
flow of control instruction—C~F
branching
halt—0
loop with branching
self-modifying code
TOY VM
booting—using a small program, load input into M[00] ∼ M[F**F] to start the machine
assembler—run assembly-language
assembly-language—use symbolic name for operation and addresses
interpreter—directly execute instruction written in a programming language
compiler—transform source code into another computer language
bootstrapping—use one virtual machine to create more powerful machine
Boolean logic
Boolean function and notation
NOT(x) ¬x x’
AND(x,y) x∧y xy
OR(x,y) x∨y x+y
XOR(x,y) x⊕y x⊕y
truth table
Boolean arithmic
absorption—x(x + y) = x + xy = x
DeMorgan’s laws—(xy)’ = x’ + y’ (x + y)’ = x’y’
Boolean function of more variables
majority—MAJ(…) = 1 iff more 1 than 0
odd-parity—ODD(…) = 1 iff number of 1 is odd
sum-of-products representation—OR(AND(each of the cases that contribute to 1)…)
circuit—interconnected network of wires, power connections, and control switchs that take value from input wire and output via output wire
control switch
relay—control line with electromagnet
vacuum tube
transistor
gates
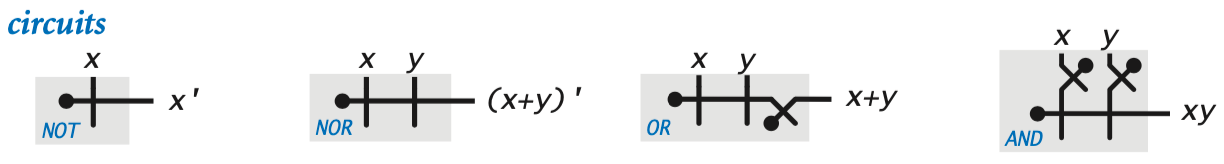
recursive definition—a gate or a network of circuits that are connected with wires
combinational circuit—no loop
output depend only on input
decoder—tell which output wire to activate
n input, 2n output
demultiplexer (demux)—add another input to decoder
add AND gate to decoder output
act as 1-to-2n logical switch
multiplexer (mux)—AND all corresponding input and OR all of those
n + 2n input wires, 1 output wire
act as 2n-to-1 logical switch
sum-of-product circuit
ALU
module—parts of the computer
bus—group of wires to transmit data between modules
sequential circuit
buzzer
flip-flop
set
reset
register
memory
bit-slice design—same circuit for demux to write and mux to read
clock
tick-tock
clock speed
fetch and execute complementary
run and halt input
CPU
control
fetch
fetch write
execute
execute write